CAMPCRAFT
(In treating of camping there has been an intentional omission of the long-term camp. This is treated extensively in the books of reference given at the close of this chapter.)
Hiking and Over-night Camp
By H. W. Gibson, Boys’ Work Secretary,
Young Men’s Christian Association
Massachusetts and Rhode Island
Several things should be remembered when going on a hike: First, avoid long distances. A foot-weary, muscle-tired and temper-tried, hungry group of boys is surely not desirable. There are a lot of false notions about courage and bravery and grit that read well in print, but fail miserably in practice, and long hikes for boys is one of the most glaring of these notions. Second, have a leader who will set a good easy pace, say two or three miles an hour, prevent the boys from excessive water drinking, and assign the duties of pitching camp, etc. Third, observe these two rules given by an old woodsman: (1) Never walk over anything you can walk around; (2) never step on anything that you can step over. Every time you step on anything you lift the weight of your body. Why lift extra weight when tramping? Fourth, carry with you only the things absolutely needed, rolled in blankets, poncho army style.
Before starting on a hike, study carefully the road maps, and take them with you on the walk for frequent reference. The best maps are those of the United States Geological Survey, costing five cents each. The map is published in atlas sheets, each sheet representing a small, quadrangular district. Send to the superintendent of documents at Washington, D. C., for a list.
For tramping the boy needs the right kind of a shoe, or the trip will be a miserable failure. A light-soled or a light-built shoe is not suited for mountain work or even for an ordinary hike. The feet will blister and become “road weary.” The shoe must be neither too big, too small, nor too heavy, and be amply broad to give the toes plenty of room. The shoe should be water-tight. A medium weight, high-topped lace shoe is about right. Bathing the feet at the springs and streams along the road will be refreshing, if not indulged in too frequently. {146} See Chapter on “Health and Endurance” for care of the feet and proper way of walking.
It is well to carry a spare shirt hanging down the back with the sleeves tied around the neck. Change when the shirt you are wearing becomes too wet with perspiration.
The most practical and inexpensive pack is the one made for the Boy Scouts of America. (Price 60 cents.) It is about 14 x 20 inches square, and 6 inches thick, made of water-proof canvas with shoulder-straps, and will easily hold everything needed for a tramping trip.
A few simple remedies for bruises, cuts, etc., should be taken along by the leader. You may not need them and some may poke fun at them, but, as the old lady said, “You can’t always sometimes tell.” The amount and kind of provisions must be determined by the locality and habitation.
The Lean-to
Fig. 1. Frame of lean-to
Reach the place where you are going to spend the night in plenty of time to build your lean-to, and make your bed for {147} the night. Select your camping spot with reference to water, wood, drainage, and material for your lean-to. Choose a dry, level place, the ground just sloping enough to insure the water running away from your lean-to in case of rain. In building your lean-to look for a couple of good trees standing from eight to ten feet apart with branches from six to eight feet above the ground. By studying the illustration (No. 1) you will be able to build a very serviceable shack, affording protection from the dews and rain. While two or more boys are building the shack, another should be gathering firewood and preparing the meal, while another should be cutting and bringing in as many soft, thick tips of trees as possible, for the roof of the shack and the beds.
How to thatch the lean-to is shown in illustration No. 2. If the camp site is to be used for several days, two lean-tos may be built facing each other, about six feet apart. This will make a very comfortable camp, as a small fire can be built between the two thus giving warmth and light.
Fig. 2. Method of thatching
The Bed
On the floor of your lean-to lay a thick layer of the fans or branches of a balsam or hemlock, with the convex side up, and the butts of the stems toward the foot of the bed. Now thatch this over with more fans by thrusting the butt ends through the first layer at a slight angle toward the head of the bed, so that the soft tips will curve toward the foot of the bed, and be sure to make the head of your bed away from the opening of the lean-to and the foot toward the opening. Over this bed spread your rubber blankets or ponchos with rubber side down, your sleeping blanket on top, and you will be surprised how soft, springy, and fragrant a bed you have, upon which to rest your “weary frame” and sing with the poet:
And trickle the white moonbeams
To my face on the balsam where I lie
While the owl hoots at my dreams.”
–J. George Frederick.
Hot-Stone Wrinkle
If the night bids fair to be cold, place a number of stones about six or eight inches in diameter near the fire, so that they will get hot. These can then be placed at the feet, back, etc., as needed, and will be found good “bed warmers.” When a stone loses its heat, it is replaced near the fire and a hot one taken. If too hot, wrap the stone in a shirt or sweater or wait for it to cool off.
Boys desire adventure. This desire may be gratified by the establishment of night watchers in relays of two boys each, every two hours. Their imaginations will be stirred by the resistless attraction of the camp-fire and the sound of the creatures that creep at night.
Observation Practice
Many boys have excellent eyes, but see not, and good ears but hear not, all because they have not been trained to observe or to hear quickly. A good method of teaching observation while on a hike or tramp is to have each boy jot down in a small note-book or diary of the trip, the different kinds of trees, birds, animals, tracks, nature of roads, fences, peculiar rock formation, smells of plants, etc., and thus be able to tell what he saw or heard to the boys upon his return to the permanent camp or to his home.
Camera Snap Shots
One of the party should take a small folding camera. Photographs of the trip are always of great pleasure and memory revivers. A practical and convenient method of carrying small folding cameras represents an ordinary belt to which a strap with a buckle has been attached, which is run through the loops at the back of the camera case. The camera may be pushed around the belt to the point where it will be least in the way.
Camp Lamp
A very convenient lamp to use on a hike is the Baldwin Camp Lamp made by John Simmons Co., 13 Franklin Street, New York City. It weighs only five ounces when full; is charged with carbide and is but 4-3/4 inches high. It projects a strong light 150 feet through the woods. A stiff wind will not blow it out. It can be worn comfortably in your hat or belt.
Handy Articles
A boy of ingenuity can make a number of convenient things. A good drinking cup may be made from a piece of bark cut {149} in parallelogram shape twisted into pyramid form and fastened with a split stick. A flat piece of bark may serve as a plate. A pot lifter may be made from a green stick about 18 inches long, allowing a few inches of a stout branch to remain. By reversing the same kind of stick and driving a small nail near the other end or cutting a notch in it, it may be used to suspend a kettle over a fire. A novel candlestick is made by opening the blade of a knife and jabbing it into a tree; upon the other upturned blade put a candle. A green stick having a split which will hold a piece of bread or meat makes an excellent broiler. Don’t pierce the bread or meat. Driving a good-sized stake into the ground at an angle of 45 degrees and cutting a notch on which may be suspended a kettle over a fire will provide a way of boiling water quickly.
Building the Fireplace
Take two or three stones and build a fireplace, a stick first shaved and then whittled for shavings, a lighted match, a little blaze, some bark and dry twigs added, a few small sticks, place the griddle over the fire and you are ready to cook the most appetizing griddle-cakes. After the cakes are cooked, fry slices of bacon upon the griddle; in the surplus fat fry slices of bread, then some thinly sliced raw potatoes done to a delicious brown. Here is a breakfast capable of making the mouth of a camper water.
Another way: Place the green logs side by side, closer together at one end than the other. Build the fire between. On the logs over the fire you can rest a frying-pan, kettle, etc. To start the fire have some light, dry wood split up fine. When sticks begin to blaze, add a few more of larger size and continue until you have a good fire. To prevent the re-kindling of the fire after it is apparently out, pour water over it and soak the earth for the space of two or three feet around it. This is very important, for many forest fires have started through failure to observe this caution.
COOKING RECEIPTS
Cooking for Hikes and Over-night Camps
The following tested receipts are given for those who go on hikes and over-night camps:
Griddle-cakes
Beat one egg, tablespoonful of sugar, one cup diluted condensed milk or new milk. Mix enough self-raising flour to {150} make a thick cream batter. Grease the griddle with rind or slices of bacon for each batch of cakes. Be sure to have the griddle hot.
Bacon
Slice bacon quite thin; remove the rind, which makes slices curl up. Fry on griddle or put on a sharp end of a stick and hold over the hot coals, or better yet remove the griddle, and put on a clean, flat rock in its place. When hot lay the slices of bacon on the rock and broil. Keep turning so as to brown on both sides.
Canned Salmon on Toast
Dip slices of stale bread into smoking hot lard. They will brown at once. Drain them. Heat a pint of salmon, picked into flakes, season with salt and pepper and turn in a tablespoonful of melted butter. Heat in a pan. Stir in one egg, beaten light, with three tablespoonfuls evaporated milk not thinned. Pour the mixture on the fried bread.
Roast Potatoes
Wash and dry potatoes thoroughly, bury them deep in a good bed of coals, cover them with hot coals until well done. It will take about forty minutes for them to bake. Then pass a sharpened hard-wood sliver through them from end to end, and let the steam escape and use immediately as a roast potato soon becomes soggy and bitter.
Baked Fresh Fish
Clean well. Small fish should be fried whole with the back bone severed to prevent curling up; large fish should be cut into pieces, and ribs loosened from back bone so as to lie flat in pan. Rub the pieces in corn meal or powdered crumbs, thinly and evenly (that browns them), fry in plenty of hot fat to a golden brown, sprinkling lightly with salt just as the color turns. If fish has not been wiped dry it will absorb too much grease. If the frying fat is not very hot when fish are put in, they will be soggy with it.
Frogs’ Legs
First, after skinning, soak them an hour in cold water to which vinegar has been added, or put them for two minutes into scalding water that has vinegar in it. Drain, wipe dry, and cook. {151} To fry: roll in flour, season with salt and pepper, and fry not too rapidly, preferably in butter or oil. Water-cress is a good relish with them. To griddle: Prepare three tablespoonsful melted butter, one half tablespoonful salt, and a pinch or two of pepper, into which dip the frogs’ legs, then roll in fresh bread crumbs and broil for three minutes on each side.
Eggs
Boiled: Have water to boiling point. Place eggs in carefully. Boil steadily for three minutes if you wish them soft. If wanted hard boiled, put them in cold water, bring to a boil, and keep it up for twenty minutes. The yolk will then be mealy and wholesome.
Fried: Melt some butter or fat in frying-pan; when it hisses drop in eggs carefully. Fry them three minutes.
Scrambled: First stir the eggs up and after putting some butter in the frying-pan, stir the eggs in it after adding a little condensed milk.
Poached: First put in the frying-pan sufficient diluted condensed milk which has been thinned with enough water to float the eggs in, and let them simmer three or four minutes. Serve the eggs on slices of buttered toast, pouring on enough of the milk to moisten the toast.
Coffee
For every cup of water allow a tablespoonful of ground coffee, then add one extra. Have water come to boiling point first, add coffee, hold it just below boiling point for five minutes, and settle with one fourth of a cup of cold water. Serve. Some prefer to put the coffee in a small muslin bag loosely tied.
Cocoa
Allow a teaspoonful of cocoa for every cup of boiling water. Mix the powdered cocoa with water or boiled milk, with sugar to taste. Boil two or three minutes.
These receipts have been tried out. Biscuit and bread making have been purposely omitted. Take bread and crackers with you from camp. “Amateur” biscuits are not conducive to good digestion or happiness. Pack butter in small jar: cocoa, sugar, and coffee in small cans or heavy paper; also salt and pepper. Wrap bread in a moist cloth to prevent drying up; {152} bacon and dried or chipped beef in wax paper. Pickles can be purchased put up in small bottles. Use the empty bottle as candle-stick.
Sample Menu for an Over-night Camp and a Day Hike or Tramp
1 pound butter
1 dozen eggs
1/2 pound cocoa
1/2 pound coffee
1 pound sugar
3 cans salmon
24 potatoes
2 cans condensed milk
1 small package of self-raising flour
Salt and pepper
Utensils
Small griddle
Small stew pan
Small coffee-pot
Large spoon
Plate and cup
Matches and candle.
Dish Washing
First fill the frying-pan with water, place over the fire, and let it boil. Pour out water and you will find the pan has practically cleaned itself. Clean the griddle with sand and water. Greasy knives and forks may be cleaned by jabbing {153} them into the ground. After all grease is gotten rid of, wash in hot water and dry with cloth. Don’t use the cloth first and get it greasy.
Leadership
The most important thing about a camping party is that it should always have the best of leadership. No group of boys should go camping by themselves. The first thing a patrol of scouts should do when it has determined to camp is to insist upon the scout master accompanying the members of the patrol. The reason for this is that there is less likely to be accidents of the kind that will break up your camp and drive you home to the town or city. When the scout master is one of the party, all of the boys can go in swimming when the proper time comes for such exercise, and the scout master can stay upon the bank or sit in the boat for the purpose of preventing accidents by drowning. There are also a hundred and one things which will occur in camp when the need of a man’s help will show itself. A scout ought to insist on his scout master going to camp. The scout master and patrol leader should be present, in order to settle the many questions which must of necessity arise, so that there may be no need of differences or quarrels over disputed points, which would be sure to spoil the outing.
Scout Camp Program
In a scout camp there will be a regular daily program, something similar to the following:
| 6:30 A.M. | Turn out, bathe, etc. |
| 7:00 A.M. | Breakfast |
| 8:00 A.M. | Air bedding in sun, if possible, and clean camp ground |
| 9:00 A.M. | Scouting games and practice |
| 11:00 A.M. | Swimming |
| 12:00 P.M. | Dinner |
| 1:00 P.M. | Talk by leader |
| 2:00 P.M. | Water games, etc. |
| 6:00 P.M. | Supper |
| 7:30 P.M. | Evening council around camp fire. |
Order of Business
| 1. | Opening Council |
| 2. | Roll-call |
| 3. | Record of last council |
| 4. | Reports of scouts |
| 5. | Left over business |
| 6. | Complaints |
| 7. | Honors |
| 8. | New scouts |
| 9. | New business |
| 10. | Challenges |
| 11. | Social doings, songs, dances, stories |
| 12. | Closing Council (devotional services when desired) 8:45 lights out |
Water Supply
Dr. Charles E. A. Winslow, the noted biologist, is authority for the following statement: “The source of danger in water is always human or animal pollution. Occasionally we find water which is bad to drink on account of passage through the ground or on account of passage through lead pipes, but the danger is never from ordinary decomposing vegetable matter. If you have to choose between a bright clear stream which may be polluted at some point above and a pond full of dead leaves and peaty matter, but which you can inspect all around and find free from contamination, choose the pond. Even in the woods it is not easy to find surface waters that are surely protected and streams particularly are dangerous sources of water supply. We have not got rid of the idea that running water purifies itself. It is standing water which purifies itself, if anything does, for in stagnation there is much more chance for the disease germs to die out. Better than either a pond or stream, unless you can carry out a rather careful exploration of their surroundings, is ground water from a well or spring; though that again is not necessarily safe. If the well is in good, sandy soil, with no cracks or fissures, even water that has been polluted may be well purified and safe to drink. In a clayey or rocky region, on the other hand, contaminating material may travel for a considerable distance under the ground. Even if the well is protected below, a very important point to look after is the pollution from the surface. I believe more cases of typhoid fever from wells are due to surface pollution than to the character of the water itself. There is danger which can, of course, be done away with by protection of the well from surface drainage, by seeing that the surface wash is not allowed to drain toward it, and that it is protected by a tight covering from the entrance of its own waste water. If good water cannot be secured in any of these ways, it must in some way be purified. … Boiling will surely destroy all disease germs.”
The Indians had a way of purifying water from a pond or swamp by digging a hole about one foot across and down about six inches below the water level, a few feet from the pond. After it was filled with water, they bailed it out quickly, repeating the bailing process about three times. After the third bailing the hole would fill with filtered water. Try it.
Sanitation
A most important matter when in camp, and away from modern conveniences is that of sanitation. This includes not only {155} care as to personal cleanliness, but also as to the water supply and the proper disposal of all refuse through burial or burning. Carelessness in these matters has been the cause of serious illness to entire camps and brought about many deaths. In many instances the loss of life in the armies has been greater through disease in the camp than on the battlefields.
Typhoid fever is one of the greatest dangers in camping and is caused by unclean habits, polluted water, and contaminated milk, and food. The armies of the world have given this disease the most careful study with the result that flies have been found to be its greatest spreaders. Not only should all sources of water supply be carefully examined, an analysis obtained if possible before use, but great care should also be taken when in the vicinity of such a supply, not to pollute it in any way. In districts where typhoid is at all prevalent it is advisable for each scout to be immunized before going to camp.
A scout’s honor will not permit him to disobey in the slightest particular the sanitary rules of his camp. He will do his part well. He will do everything in his power to make his camp clean, sanitary, and healthful from every standpoint.
General Hints
Water Hints
If you work your hands like paddles and kick your feet, you can stay above water for some time even with your clothes on. It requires a little courage and enough strength not to lose your head.
Ready for the hike
Many boy swimmers make the mistake of going into the water too soon after eating. The stomach and digestive organs are busy preparing the food for the blood and body. Suddenly they are called upon to care for the work of the swimmer. The change is too quick for the organs, the process of digestion stops, congestion is apt to follow, and then paralyzing cramps.
Indian Bathing Precaution
The Indians have a method of protecting themselves from cramps. Coming to a bathing pool, an Indian swimmer, after stripping off, and before entering the water, vigorously rubs the pit of the stomach with the dry palm of his hands. This rubbing probably takes a minute, then he dashes cold water all over his stomach and continues the rubbing for another minute, and after that he is ready for his plunge. If the water in which you are going to swim is cold, try this method before plunging into the water.
Good Bathing Rule
The rule in most camps regarding entering the water is as follows: “No one of the party shall enter the water for swimming or bathing except at the time and place designated, and in the presence of a leader.” Laxity in the observance of this rule will result disastrously.
Clouds
Every cloud is a weather sign: Low clouds, swiftly moving, indicate coolness and rain; hard-edged clouds, wind; rolled or jagged clouds, strong wind; “mackerel” sky, twelve hours day.
Smoke beats downward.
Sun is red in the morning.
There is a pale yellow or greenish sunset.
Rains
A sudden shower is soon over.
A slow rain lasts long.
Rain before seven, clear before eleven.
A circle round the moon means “storm.”
Sets the traveler on his way;
The evening gray, the morning red
Brings down showers upon his head.”
Look for rain before the light.”
Look for rain before the night.”
Clear
Rain will never come to pass.”
West wind brings clear, bright, and cool weather.
North wind brings cold.
South wind brings heat.
Direction of the Wind
The way to find which way the wind is blowing is to throw up little bits of dry grass, or to hold up a handful of light dust and let it fall, or to suck your thumb, wet it all around and let the wind blow over it, and the cold side of it will then tell you which way the wind is blowing.
Weather Flags
The United States Weather Bureau publishes a “Classification of Clouds” in colors, which may be had for the asking. If you are near one of the weather signal stations, daily bulletins will be sent to camp upon request; also the weather map.
A set of flag signals run up each day will create interest. The flags are easily made or may be purchased.
Keep a daily record of temperature. A boy in charge of the “weather bureau” will find it to be full of interest as well as offering an opportunity to render the camp a real service. He will make a weather vane, post a daily bulletin, keep a record of temperature, measure velocity of wind, and rainfall.
How to Get Your Bearings
If you have lost your bearings, and it is a cloudy day, put the point of your knife blade on your thumb nail, and turn the blade around until the full shadow of the blade is on the nail. This will tell you where the sun is, and decide in which direction the camp is.
Face the sun in the morning, spread out your arms straight {158} from body. Before you is the east; behind you is the west; to your right is the south; the left hand is the north. Grass turns with the sun. Remember this when finding your way at night.
Building a Camp Fire
There are ways and ways of building a camp fire. An old Indian saying runs, “White man heap fool, make um big fire–can’t git near! Injun make um little fire–git close! Ugh! good!”
Make it a service privilege for a tent of boys to gather wood and build the fire. This should be done during the afternoon. Two things are essential in the building of a fire–kindling and air. A fire must be built systematically. First, get dry, small, dead branches, twigs, fir branches, and other inflammable material. Place these on the ground. Be sure that air can draw under it and upward through it. Next place some heavier sticks and so on until you have built the camp fire the required size. An interesting account of “How to Build a Fire by Rubbing Sticks,” by Ernest Thompson Seton, will be found in Chapter 11. In many camps it is considered an honor to light the fire.
Never build a large camp fire too near the tent or inflammable pine trees. Better build it in the open.
Be sure and use every precaution to prevent the spreading of fire. This may be done by building a circle of stones around the fire, or by digging up the earth, or by wetting a space around the fire. Always have the buckets of water near at hand. To prevent the re-kindling of the fire after it is apparently out, pour water over it and soak the earth for a space of two or three feet around it. This is very important, for many forest fires have started through failure to observe this caution.
Things to remember: First, it is criminal to leave a burning fire; second, always put out the fire with water or earth.
“A fire is never out,” says Chief Forester H. S. Graves, “until the last spark is extinguished. Often a log or snag will smolder unnoticed after the flames have apparently been conquered only to break out afresh with a rising wind.”
Be sure to get a copy of the laws of your state regarding forest fires, and if a permit is necessary to build a fire, secure it, before building the fire.
Kephart, in his book on “Camping and Woodcraft” (p. 28), says: “When there is nothing dry to strike it on, jerk the head {160} of the match forward through the teeth. Or, face the wind. Cup your hands back toward the wind, remove the right hand just long enough to strike the match on something very close by, then instantly resume former position. Flame of match will run up stick instead of blowing away from it.”
|
FOREST FIRES!
The great annual destruction of forests by fire is an injury to all persons and industries. The welfare of every community is dependent upon a cheap and plentiful supply of timber, and a forest cover is the most effective means of preventing floods and maintaining a regular flow of streams used for irrigation and other useful purposes. To prevent forest fires Congress passed the law approved May 5, 1900, which– Forbids setting fire to the woods, and Forbids leaving any fires unextinguished. This law, for offenses against which officers of the FOREST SERVICE can arrest without warrant, provides as maximum punishment– A fine of $5000, or imprisonment for two years, or both, if a fire is set maliciously, and A fine of $1000, or imprisonment for one years, or both, if a fire is set carelessly, It also provides that the money from such fines shall be paid to the school fund of the county in which the offense is committed. THE EXERCISE OF CARE WITH SMALL FIRES IS THE BEST PREVENTIVE OF LARGE ONES. Therefore all persons are requested– 1. Not to drop matches or burning tobacco where there is inflammable material. 2. Not to build larger camp fires than are necessary. 3. Not to build fires in leaves, rotten wood, or other places where they are likely to spread. 4. In windy weather and in dangerous places, to dig holes or clear the ground to confine camp fires. 5. To extinguish all fires completely before leaving them, even for a short absence. 6. Not to build fires against large or hollow logs, where it is difficult to extinguish them. 7. Not to build fires to clear land without informing the nearest officer of the FOREST SERVICE, so that he may assist in controlling them. This notice is posted for your benefit and the good of every resident of the region. You are requested to cooperate in preventing the removal or defacement, which acts are punishable by law. JAMES WILSON, |
Around the camp fire
The Camp Fire
“I cannot conceive of a camp that does not have a big fire. Our city houses do not have it, not even a fireplace. The fireplace is one of the greatest schools the imagination has ever had or can ever have. It is moral, and it always has a tremendous stimulus to the imagination, and that is why stories and fire go together. You cannot tell a good story unless you tell it before a fire. You cannot have a complete fire unless you have a good story-teller along!
“There is an impalpable, invisible, softly stepping delight in the camp fire which escapes analysis. Enumerate all its charms and still there is something missing in your catalogue.
“Anyone who has witnessed a real camp fire and participated in its fun as well as seriousness will never forget it. The huge fire shooting up its tongue of flame into the darkness of the night, the perfect shower of golden rain, the company of happy {161} boys, and the great dark background of piny woods, the weird light over all, the singing, the yells, the stories, the fun, and then the serious word at the close, is a happy experience long to be remembered.”
Camp-fire Stunts
The camp fire is a golden opportunity for the telling of stories–good stories told well. Indian legends, war stories, ghost stories, detective stories, stories of heroism, the history of life, a talk about the stars. Don’t draw out the telling of a story. Make the story life-like.
College songs always appeal to boys. Let some leader start up a song in a natural way, and soon you will have a chorus of unexpected melody and harmony. As the fire dies down, let the songs be of a more quiet type like “My Old Kentucky Home,” and ballads of similar nature.
When the embers are glowing is the time for toasting marshmallows. Get a long stick sharpened to a point, fasten a marshmallow on the end, hold it over the embers, not in the blaze, until the marsh-mallow expands. Oh, the deliciousness of it! Ever tasted one? Before roasting corn on the cob, tie the end of the husk firmly with string or cord; soak in water for about an hour; then put into the hot embers. The water prevents the corn from burning and the firmly tied husks enable the corn to be steamed and the real corn flavor is thus retained. In about twenty minutes the corn may be taken from the fire and eaten. Have a bowl of melted butter and salt at hand. Also a pastry brush to spread the melted butter upon the corn. Try it.
Story Telling
For an example of a good story to be told around the camp fire this excellent tale by Prof. F. M. Burr is printed by permission:
How Men Found the Great Spirit
In the olden time, when the woods covered all the earth except the deserts and the river bottoms, and men lived on the fruits and berries they found and the wild animals which they could shoot or snare, when they dressed in skins and lived in caves, there was little time for thought. But as men grew stronger and more cunning and learned how to live together, they had more time to think and more mind to think with.
Men had learned many things. They had learned that cold weather followed hot; and spring, winter; and that the sun got up in the morning and went to bed at night. They said that the great water was kindly when the sun shone, but when the sun hid its face and the wind blew upon it, it grew black and angry and upset their canoes. They found that knocking flints together or rubbing dry sticks would light the dry moss and that the {162} flames which would bring back summer in the midst of winter and day in the midst of night were hungry and must be fed, and when they escaped devoured the woods and only the water could stop them.
These and many other things men learned, but no one knew why it all was or how it came to be. Man began to wonder, and that was the beginning of the path which led to the Great Spirit.
In the ages when men began to wonder there was born a boy whose name was Wo, which meant in the language of his time, “Whence.” As he lay in his mother’s arms she loved him and wondered: “His body is of my body, but from whence comes the life–the spirit which is like mine and yet not like it?” And his father seeing the wonder in the mother’s eyes, said, “Whence came he from?” And there was no one to answer, and so they called him Wo to remind them that they knew not from whence he came.
As Wo grew up, he was stronger and swifter of foot than any of his tribe. He became a mighty hunter. He knew the ways of all the wild things and could read the signs of the seasons. As he grew older they made him a chief and listened while he spoke at the council board, but Wo was not satisfied. His name was a question and questioning filled his mind.
“Whence did he come? Whither was he going? Why did the sun rise and set? Why did life burst into leaf and flower with the coming of spring? Why did the child become a man and the man grow old and die?”
The mystery grew upon him as he pondered. In the morning he stood on a mountain top and stretching out his hands cried, “Whence?” At night he cried to the moon “Whither?” He listened to the soughing of the trees and the song of the brook and tried to learn their language. He peered eagerly into the eyes of little children and tried to read the mystery of life. He listened at the still lips of the dead, waiting for them to tell him whither they had gone.
He went out among his fellows silent and absorbed, always looking for the unseen and listening for the unspoken. He sat so long silent at the council board that the elders questioned him. To their questioning he replied like one awakening from a dream:
“Our fathers since the beginning have trailed the beasts of the woods. There is none so cunning as the fox, but we can trail him to his lair. Though we are weaker than the great bear and buffalo, yet by our wisdom we overcome them. The deer is more swift of foot, but by craft we overtake him. We cannot fly like a bird, but we snare the winged one with a hair. We have made ourselves many cunning inventions by which the beasts, the trees, the wind, the water and the fire become our servants.
“Then we speak great swelling words: ‘How great and wise we are! There is none like us in the air, in the wood, or in the water!’
“But the words are false. Our pride is like that of a partridge drumming on his log in the wood before the fox leaps upon him. Our sight is like that of the mole burrowing under the ground. Our wisdom is like a drop of dew upon the grass. Our ignorance is like the great water which no eye can measure.
“Our life is like a bird coming out of the dark, fluttering for a heart-beat in the tepee and then going forth into the dark again. No one can tell whence it comes or whither it goes. I have asked the wise men and they cannot answer. I have listened to the voice of the trees and wind and water, but I do not know their tongue; I have questioned the sun and the moon and the stars, but they are silent.
“But to-day in the silence before the darkness gives place to light, I seemed to hear a still small voice within my breast, saying to me, ‘Wo, the {163} questioner, rise up like the stag from his lair; away, alone, to the mountain of the sun. There thou shalt find that which thou seekest.’ I go, but if I fail by the trail another will take it up. If I find the answer I will return.”
Waiting for none, Wo left the council of his tribe and went his way toward the mountain of the sun. For six days he made his way through the trackless woods, guided by the sun by day and the stars by night. On the seventh day he came to the great mountain–the mountain of the sun, on whose top, according to the tradition of his tribe, the sun rested each night. All day long he climbed saying to himself, “I will sleep tonight in the teepee of the sun, and he will tell me whence I come and whither I go.”
But as he climbed the sun seemed to climb higher and higher; and, as he neared the top, a cold cloud settled like a night bird on the mountain. Chilled and faint with hunger and fatigue, Wo struggled on. Just at sunset he reached the top of the mountain, but it was not the mountain of the sun, for many days’ journey to the west the sun was sinking in the Great Water.
A bitter cry broke from Wo’s parched lips. His long trail was useless. There was no answer to his questions. The sun journeyed farther and faster than men dreamed, and of wood and waste and water there was no end. Overcome with misery and weakness he fell upon a bed of moss with his back toward the sunset and the unknown.
And Wo slept, although it was unlike any sleep he had ever known before, and as he slept he dreamed. He was alone upon the mountain waiting for the answer. A cloud covered the mountain but all was silent. A mighty wind rent the cloud and rushed roaring through the crags, but there was no voice in the wind. Thunder pealed, lightning flashed, but he whom Wo sought was not there.
In the hush that followed up the storm Wo heard a voice, low and quiet, but in it all the sounds of earth and sky seemed to mingle–the song of the bird, the whispering of the trees, and the murmuring of the brook.
“Wo, I am he whom thou seekest, I am the Great Spirit. I am the All Father. Ever since I made man of the dust of the earth, and so child of the earth and brother to all living, and breathed into his nostrils the breath of life, thus making him my son, I have waited for a seeker who should find me. In the fullness of time thou hast come, Wo the questioner, to the answerer.
“Thy body is of the earth and to earth returns; thy spirit is mine; it is given thee for a space to make according to thy will; then it returns to me better or worse for thy making.
“Thou hast found me because thy heart was pure, and thy search for me tireless. Go back to thy tribe and be to them the voice of the Great Spirit. From henceforth I will speak to thee, and the seekers that come after thee in a thousand voices and appear in a thousand shapes. I will speak in the voices of the woods and streams and of those you love. I will appear to you in the sun by day and the stars by night. When thy people and mine are in need and wish for the will of the Great Spirit, then shall my spirit brood over thine and the words that thou shalt speak shall be my words.”
And Wo awoke, facing the east and the rising sun. His body was warmed by its rays. A great gladness filled his soul. He had sought and found and prayer came to him like the song to the bird.
“O Great Spirit, father of my spirit, the sun is thy messenger, but thou art brighter than the sun. Drive thou the darkness before me. Be thou the light of my spirit.” As Wo went down the mountain and took the journey back to the home of his people, his face shone, and the light never seemed to leave it, so that men called him “He of the shining face.”
When Wo came back to his tribe, all who saw his face knew that he had found the answer, and they gathered again about the council fire to hear. As Wo stood up and looked into the eager faces in the circle of the fire, he remembered that the Great Spirit had given him no message and for a moment he was dumb. Then the words of the Great Spirit came to him again. “When thy people and mine shall need to know my will, my spirit shall brood over thine and the words that thou shalt speak shall be my words.” Looking into the eager faces of longing and questioning, his Spirit moved within him and he spoke:
“I went, I sought, I found the Great Spirit who dwells in the earth as your spirits dwell in your bodies. It is from Him the spirit comes. We are His children. He cares for us more than a mother for the child on her breast, or the father for the son that is his pride. His love is like the air we breathe: it is about us; it is within us.
“The sun is the sign of His brightness, the sky of His greatness and mother-love and father-love, and the love of man and woman are the signs of His love. We are but His children; we cannot enter into the council of the Great Chief until we have been proved, but this is His will, that we love one another as He loves us; that we bury forever the hatchet of hate, that no man shall take what is not his own and the strong shall help the weak.”
The chiefs did not wholly understand the words of Wo, but they took a hatchet and buried it by the fire saying, “Thus bury we hate between man and his brother,” and they took an acorn and put it in the earth saying, “Thus plant we the love of the strong for the weak.” And it became the custom of the tribe that the great council in the spring should bury the hatchet and plant the acorn. Every morning the tribe gathered to greet the rising sun, and with right hand raised and left upon their hearts prayed: “Great Spirit hear us; guide us to-day; make our wills Thy will, our ways Thy way.”
And the tribe grew stronger and greater and wiser than all the other tribes–but that is another story.
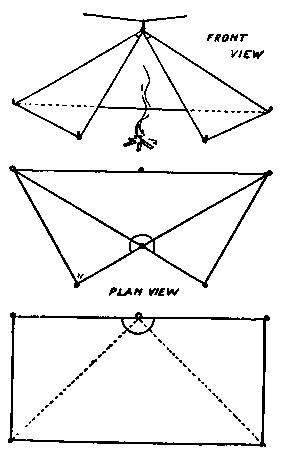
Tent Making Made Easy
By H. J. Holden
(Reprinted from Recreation. Apr. 1, 1911. by permission of the Editor.)
The accompanying sketches show a few of the many different tents which may be made from any available piece of cloth or canvas. The material need not be cut, nor its usefulness for other purposes impaired, except that rings or tapes are attached at various points as indicated. For each tent the sketches show a front elevation, with a ground plan, or a side view; also a view of the material laid flat, with dotted lines to indicate where creases or folds will occur. Models may be made from stiff paper and will prove as interesting to the kindergartner in geometry as to the old campaigner in camping. In most of the tents a ring for suspension is fastened at the centre of one side. This may be supported by a pole or hung by means {165} of a rope from any convenient fastening; both methods are shown in the sketches. Guy ropes are required for a few of the different models, but most of them are pegged down to the ground.
After making paper models, find a stack cover, a tarpaulin, a tent fly, an awning, or buy some wide cotton cloth, say 90-inch. All the shapes may be repeatedly made from the same piece of material, if the rings for changes are left attached. In Nos. 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, a portion of the canvas is not used and may be turned under to serve as sod-cloth, or rolled up out of the way. If your material is a large piece, more pegs and guy lines will be required than is indicated in the sketches. The suspension ring, 1-1/2 inches or 2 inches in diameter, should be well fastened, with sufficient reinforcement to prevent tearing out; 1-inch rings fastened with liberal lengths of tape are large enough for the pegs and guy lines. Also reinforce along the lines of the strain from peg to pole.
Fig. 1.–A square of material hung by one corner, from any convenient support, in a manner to make a comfortable shelter; it will shed rain and reflect heat. This square makes a good fly or a good ground cloth for any of the tents.
Fig. 1. Tent from a square of canvas.
7 x 7 sheet is ample for a one-man shelter; 9 x 9 will house two.
Fig. 2.–A rectangle equal to two squares. A shelter roomy and warm, with part of one side open toward the fire.
Fig. 2. Rectangle tent
Fig. 3.–Here the rectangle is folded to make a “lean-to” shelter, with the roof front suspended from a rope or from a horizontal pole by means of cords. The two corners not in use are folded under, making a partial ground cloth. A square open front is presented toward the camp fire.
Fig. 3. Baker, or lean-to
Fig. 4.–Same in plan as No.3, but has a triangular front and only one point of suspension.
Fig. 4. Same plan as No.3
Fig 5.–Uses all the cloth, has a triangular ground plan, a square front opening, plenty of head room at the back and requires two or more guy lines. This shelter resembles a “toque.”
Fig. 5. The toque tent
Fig. 6.–Square or “miner’s” tent. Two corners are turned under. This tent is enclosed on all sides, with a door in front.
Fig. 6. Miner’s tent
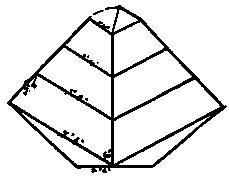
Fig. 7.–Conical tent or “wigwam,” entirely enclosed, with door in front. Two corners of the canvas are turned under.
Fig. 7. Conical tent, or wigwam
Fig. 8.–Has a wall on one side and is called a “canoe tent” in some catalogues. It requires two or more guy lines and is shown with a pole support. The front has a triangular opening.
Fig. 8. So-called canoe tent. Requires three guy lines,
and can be supported by a rope instead of a pole
Fig. 9.–A combination of No. 8, with No. 1 in use as an awning or fly. This sketch shows both tent and fly suspended by means of a rope. The “awning” may be swung around to any angle.
Fig. 9. Canoe tent with fly
Fig. 10.–Combination of Nos. 1 and 2; they may be fastened together by a coarse seam or tied with tapes. The ground plan is an equal-sided triangle, with a door opening on one side, as shown. There is no waste cloth.
Fig. 10. Combination of Nos. 1 and 2
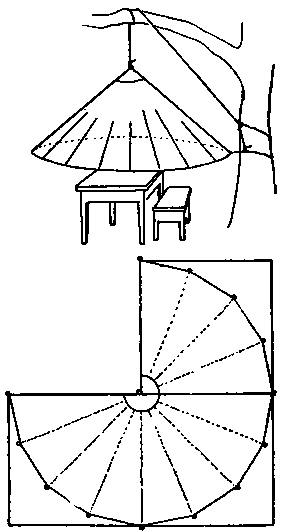
Fig. 11.–No. 10 changed to a conical shape and suspended as a canopy. The circular shape is secured by the use of small-size gas pipe or limber poles bent into a large hoop. Of course guy lines may be used, but would probably be in the way. Notice that a little more material for making a wall would transform the canopy into a “Sibley” tent.
Fig. 11. Sibley awning
There are other shapes and combinations, but perhaps these sketches are enough in the line of suggestion.
The diagram Fig. 12 shows a method for laying out, on your cloth, the location of all the rings to make the tents and shelters. No dimensions are given and none is required. The diagram is good for any size. Most of the fastenings are found on radial lines, which are spaced to divide a semi-circle into eight equal {169} angles, 22-1/2 degrees each; these intersect other construction lines and locate the necessary loops and rings. Figures are given at each ring which refer back to the sketch numbers.
Fig. 12. Showing how ten different tents can be made with but one piece of canvas
Suppose the material at hand is the widest unbleached cotton cloth, 90 inches wide, 5 yards long, or 7-1/2 feet by 15 feet. The accompanying table will give the dimensions for the various shapes from Fig. 1 to Fig. 11.
If in doubt about the location of rings on your canvas, suspend the tent by the centre ring and fasten the loops temporarily by means of safety pins, draw the tent into shape and shift the fastenings as required. The guy lines should have hooks or snaps at one end for ready attachment and removal; the other end should be provided with the usual slides for “take up.” The edge of the cloth where the large ring for suspension is fastened should be bound with tape or have a double hem, for it is the edge of the door in most of the tents shown.
| Size | Area, Sq. Ft. | Height, Ft. | Remarks | |
| 1 | 7-1/2 ft. triangle | 25 | 6-1/4 | One side open |
| 2 | 6-1/2 X 15 ft. | 65 | 6-1/4 | One side open |
| 3 | 6 x 7-1/2 ft. | 45 | 4-1/2 | One side open |
| 4 | 7-1/2 x 8 ft. | 60 | 5-1/2 | One side open |
| 5 | 7-1/2 ft. triangle | 25 | 7-1/2 | One side open |
| 6 | 6-1/4 x 6-1/4 ft. | 39 | 7 | Enclosed |
| 7 | 7-1/2 ft. diam. | 44 | 6-1/2 | Enclosed |
| 8 | 5 x 7-1/2 ft. | 37-1/2 | 6-1/2 | 2-1/2 ft. wall |
| 9 | 7-1/2 x 8 ft. | 60 | 6-1/2 | No.8, with fly |
| 10 | 15 ft. triangle | 97 | 6-1/4 | Enclosed |
| 11 | 11-1/4 ft. circle | 108 | 5 | Canopy, no sides |
Waterproofing a Tent
Dissolve half a pound of alum in two quarts of boiling water; then add two gallons of pure cold water. In this solution place the material and let it remain for a day. Dissolve a quarter of a pound of sugar of lead in two quarts boiling water, then add two gallons of cold water. Take the material from the alum solution, wring it lightly, place in the second solution and leave for five or six hours; then wring out again lightly and allow it to dry.
If you want to avoid trouble with a leaky tent, the following solution is a “sure cure;” Take a gallon or two gallons of turpentine and one or two cakes of paraffin, drug store size. Chip the paraffin fairly fine; dump it into the turpentine. Place the turpentine in a pail and set same in a larger pail or a tub of hot water. The hot water will heat the turpentine, and the turpentine will melt the paraffin. Stir thoroughly, and renew your supply of hot water if necessary. Then pile your tent into a tub and pour in the turpentine and paraffin mixture. Work the tent all over thoroughly with your hands, so that every fiber gets well saturated. You must work fast, however, as the paraffin begins to thicken as it cools; and work out of doors, in a breeze if possible, as the fumes of the turpentine will surely make you sick if you try it indoors. When you have the tent thoroughly saturated, hang it up to dry. It is not necessary to wring the tent out when you hang it up. Just let it drip. If you use too much paraffin the tent may look a little dirty after it dries, but it will be all right after you have used it once or twice.
An Open Outing Tent
By Warren H. Miller, Editor “Field and Stream.”
To make an open outing tent, get thirteen yards of 8 oz. duck canvas, which can be bought at any department store or dry goods store for seventeen or eighteen cents a yard. This makes your total expense $2.21 for your tent. Layout the strip of canvas on the floor and cut one end square; measure up 8 inches along the edge and draw a line to the other corner. {171} From this corner layoff 7 ft. 8 in. along the edge and on the opposite side, layoff 5 ft. 9 in. beginning at the end of your 8-in. measurement. Now take a ruler and draw another diagonal across the canvas at the ends of these measurements and you have the first gore of your tent. Cut it across, turn the gore over, lay it down on the strip so as to measure off another one exactly like it. This is the corresponding gore for the other side of the tent. To make the second pair of gores, layoff 5 ft. 9 in. along one side of the remaining strip of canvas beginning at the pointed end, and 3 ft. 10 in. on the other side. Join these points with a diagonal and you have a second gore, a duplicate of which is then cut by using it as a pattern, reversing and laying it down on the strip of canvas. To make the third gore, layoff 3 ft. 10 in, on one edge of your strip beginning at the point, and 1 ft. 11 in. on the other side. Draw a diagonal across and you have the third gore.
How to cut up your strip of canvas
Forester tent pattern
Forester tent with hood
You have now used up all but two yards of your canvas, plus a little left-over piece of about two feet long. Out of this little left-over piece make a triangle 1 ft. 11 in. on the side, which will form the back triangle of your tent. Now pin your three gores together to make the side of your tent, just as in the illustrations, and pin the two sides together along the ridge. Then sew this tent up. Sew in the little back triangle and hem all around the edges. Leave a hole at the peak of the little triangle through which the ridge pole must go.
To set it up, cut three small saplings, one of which should be twelve feet long and the other two, ten feet long. Tie these two together at the ends making what the sailors call a “shears.” Take the twelve-foot pole and run it down the ridge inside the tent, and out through the hole in the back. Now raise the ridge pole with one end stuck in the ground and the front end resting on the two shear poles and tie all three of them together. At the end of each seam along the hem you must work in a little eyelet hole for a short piece of twine to tie to the tent pegs. Stretch out the back triangle, pegging it down at the two corners on the ground, and then peg out each hole along the foot until the entire tent stretches out taut as in our illustrations. Three feet from the peak along the front edge you must have another eyelet hole with a little piece of twine and you tie this out to the shear pole on each side which gives the tent the peculiar gambrel roof which it has, and which has the advantage of giving you lots more room inside than the straight tent would. You now have what is known as the “open” forester tent.
Forester tent with hood
If a thunder storm comes up with a driving rain it will surely rain in at the front unless you turn the tent around by moving the poles one at a time. If you don’t want to do this you can make a hood for the front out of the two yards of canvas you have left. Simply draw a diagonal from one corner to the other of this {173} two-yard piece of duck and cut it down the diagonal, making two thin triangles which are sewed to the front edges of the open forester tent, making a hood of the shape shown in our picture. This prevents the rain beating in the opening of your tent but still lets the heat of your fire strike in and at the same time it keeps the heat in the tent as it will not flow out along the ridge pole as it does in the open type.
This tent weighs six pounds and packs into a little package fourteen inches long by seven inches wide by six: inches thick, and can be carried as a shoulder strap or put in a back pack or any way you wish to take it. It will sleep three boys, or two men and a boy, very comfortably indeed. While it really does not need to be water-proofed, as it immediately shrinks tight after the first rain, you can water-proof it if you wish by making a solution of ten ounces of quick lime with four ounces of alum in ten quarts of water. Stir occasionally until the lime has slackened. Put the tent in another pail and pour the solution over it, letting it stand twelve hours. Take out and hang it on the clothes-line to dry. It will then be entirely waterproof.
To make a good night fire in front of the tent, drive two stout stakes three feet long in the ground about three feet from the mouth of the tent; pile four logs one on top of the other against these stakes or take a large flat stone and rest it against it. Make two log andirons for each side of the fire and build your fire in the space between them. It will give you a fine cheerful fire and all the heat will be reflected by the back logs into the tent, making it warm and cheerful. Inside you can put your browse bags stuffed with balsam browse; or pile up a mountain of dry leaves over which you can stretch your blankets. Pile all the duffle way back in the peak against the little back triangle where it will surely keep dry and will form a sort of back for your pillows. You will find the forester tent lighter and warmer than the ordinary lean-to, as it reflects the heat better. After a couple of weeks in it you will come home with your lungs so full of ozone that it will be impossible to sleep in an ordinary room without feeling smothered.
Canoeing, Rowing and Sailing
(Prepared with the cooperation of Mr. Arthur A. Carey, Scout Master, Boy Scout ship Pioneer; Mr. Carleton E. Sholl, Captain Lakanoo Boat Club Crew; Mr. Frederick K. Vreeland, Camp-Fire Club of America. and Mr. R. F. Tims, Vice-Commodore, American Canoe Association.)
The birch-bark canoe is the boat of the North American Indians, and our modern canvas canoes are made, with some {174} variations, on the Indian model. With the possible exception of the Venetian gondola, the motion of a canoe is more graceful than that of any other boat propelled by hand; it should be continuous and gliding, and so silent that it may be brought up in the night to an animal or enemy, Indian fashion, without making any sound, and so take them by surprise.
Canoeing stroke (a)
Many accidents happen in canoes–not because they are unsafe when properly handled, but because they are unsafe when improperly handled–and many people do not take the trouble even to find out the proper way of managing a canoe. Many canoes have seats almost on a level with the gunwale, whereas, properly speaking, the only place to sit in a canoe is on the bottom; for a seat raises the body too high above the centre of gravity and makes the canoe unsteady and likely to upset. It is, however, difficult to paddle while sitting in the bottom of a canoe, and the best position for paddling is that of kneeling and at the same time resting back against one of the thwarts. The size of the single-blade paddle should be in proportion to the size of the boy who uses it–long enough to reach from the ground to the tip of his nose. The bow paddle may be a little shorter. The canoeman should learn to paddle equally well on either side of a canoe. When paddling on the {175} left side the top of the paddle should be held by the right hand, and the left hand should be placed a few inches above the beginning of the blade. The old Indian stroke, which is the most approved modern method for all-round canoeing, whether racing or cruising, is made with the arms almost straight–but not stiff–the arm at the top of the paddle bending only slightly at the elbow. This stroke is really a swing from the shoulder, in which there is little or no push or pull with the arm. When paddling on the left side of the canoe the right shoulder swings forward and the whole force of the body is used to push the blade of the paddle through the water, the left hand acting as a fulcrum. While the right shoulder is swung forward, the right hand is at the same time twisted at the wrist so that the thumb goes down; this motion of the wrist has the effect of turning the paddle around in the left hand–the left wrist being allowed to bend freely–so that, at the end of the stroke, the blade slides out of the water almost horizontally. If you should twist the paddle in the opposite direction it would force the head of the canoe around so that it would travel in a circle. At the recovery of the stroke the right shoulder swings back and the paddle is brought forward in a horizontal position, with the blade almost parallel to the water. It is swung forward until the paddle is at right angles across the canoe, then the blade is dipped edgewise with a slicing motion and a new stroke begins. In paddling on the right side of the canoe the position of the two hands and the motion of the two shoulders are reversed.
Canoeing stroke (b)
Something should also be said about double paddles–that is, paddles with two blades–one at each end–as their use is becoming more general every year. With the double paddle a novice can handle a canoe, head on to a stiff wind, a feat which {176} requires skill and experience with a single blade. The doubles give greater safety and more speed and they develop chest, arm and shoulder muscles not brought into play with a single blade. The double paddle is not to be recommended to the exclusion of the single blade, but there are many times when there is an advantage in its use.
Canoeing stroke (c)
In getting in or out of a canoe it is especially necessary to step in the very centre of the boat; and be careful never to lean on any object–such as the edge of a wharf–outside of the boat, for this disturbs your balance and may capsize the canoe. Especially in getting out, put down your paddle first, and then, grasping the gunwale firmly in each hand, rise by putting your weight equally on both sides of the canoe. If your canoe should drift away sideways from the landing-place, when you are trying to land, place the blade of your paddle flat upon the water in the direction of the wharf and gently draw the canoe up to the landing-place with a slight sculling motion.
When it is necessary to cross the waves in rough water, always try to cross them “quartering,” i. e. at an oblique angle, but not at right angles. Crossing big waves at right angles {177} is difficult and apt to strain a canoe, and getting lengthwise between the waves is dangerous. Always have more weight aft than in the bow; but, when there is only one person in the canoe, it may be convenient to place a weight forward as a balance; but it should always be lighter than the weight aft. A skillful canoeman will paddle a light canoe even in a strong wind by kneeling at a point about one third of the length from the stern.
For the purpose of sailing in a canoe the Lateen rig is the safest, most easily handled, and the best all-round sailing outfit. For a seventeen-foot canoe a sail having forty square feet of surface is to be recommended, and, in all except very high winds, this can be handled by one man.
Canoe with sail
The Lateen sail is made in the form of an equilateral triangle, and two sides are fastened to spars which are connected at one end by a hinge or jaw. The mast–which should be set well forward–should be so long that, when the sail is spread and the slanting upper spar is swung from the top of the mast, the lower spar will swing level about six to eight inches above the gunwale and hang clear above all parts of the boat in going about. The sail is hoisted by a halyard attached at, or a little above, the centre of the upper spar, then drawn through a block attached to the brace which holds the mast in position, {178} and thus to the cleats–within easy reach of the sailor. The sheet line is fastened to the lower spar, about two feet from the outer end; and, when not held in the hand, may be fastened to another cleat. Both halyard and sheet should at all times be kept clear, so as to run easily, and with knots about the cleats that can be instantly slipped.
The leeboard is a necessary attachment to the sailing outfit. It is made with two blades–about three feet long and ten inches wide would furnish a good-sized surface in the water–one dropping on each side of the canoe and firmly supported by a bar fastened to the gunwale. The blades should be so rigged that, when striking an object in the water, they will quickly release, causing no strain on the canoe. The leeboard, like a centre board, is of course intended to keep the canoe from sliding off when trying to beat up into the wind. When running free before the wind the board should be raised. The general rules for sailing larger craft apply to the canoe.
The paddle is used as a rudder and may be held by the sailor, but a better plan is to have two paddles, one over each side, made fast to the gunwale or the brace. The sailor can then grasp either one as he goes about and there is no danger of losing the paddles overboard. In sailing, the sailor sits on the bottom, on the opposite side from the sail, except in a high wind, when he sits on the gunwale where he can the better balance the sail with his weight. The combination of sail, leeboards, and the balancing weight of the sailor, will render the canoe stiff and safe, with proper care, in any wind less than a gale. A crew may consist of two or three in a seventeen foot canoe.
The spars and mast of a sailing outfit should be of spruce or some other light but strong wood, while cedar or some non-splitting wood is best for the leeboards. Young canoeists will enjoy making their own sailing outfits; or a complete Lateen rig as made by various canoe manufacturers can be purchased either directly from them or through almost any dealer.
In case of an upset the greatest mistake is to leave the boat. A capsized canoe will support at least four persons as long as they have strength to cling to it. A single man or boy, in case of upsetting beyond swimming distance to land, should stretch himself flat upon the bottom of the canoe, with arms and legs spread down over the tumblehome toward the submerged gunwales. He can thus lie in safety for hours till help arrives. When two persons are upset, they should range themselves one {179} on each side of the overturned boat; and, with one hand grasping each other’s wrists across the boat, use the other hand to cling to the keel or the gunwale. If the canoe should swamp, {180} fill with water, and begin to sink, it should be turned over in the water. It is the air remaining under the inverted hull that gives the craft sufficient buoyancy to support weight.
Never overload a canoe. In one of the ordinary size–about seventeen feet in length–three persons should be the maximum number at anytime, and remember never to change seats in a canoe when out of your depth.
This diagram illustrates some of the angles formed by the boom and the keel line of the boat in different positions:
Running free, or before the wind
Wind abeam Port tack
Wind abeam Starboard tack
Pointing into the wind Port tack
Pointing into the wind Starboard tack.

Row-boats
There is a certain caution in the use of boats which you will always find among sailors and fishermen and all persons who are using them constantly. Such a person instinctively steps into the middle of the boat when getting in, and always sits in the middle of the thwart or seat. This is a matter of instinct with seafaring people, and so is the habit of never fooling in a boat. Only landlubbers will try to stand up in a small boat while in motion; and, as for the man who rocks a boat “for fun,” he is like the man “who didn’t know the gun was loaded.”
Rowing
Row-boats are propelled either by rowing or by sculling; and rowing is either “pulling” or “backing water.” The usual way of rowing is to “pull” and to do so, you sit with your back to the bow and propel the boat by pulling the handles toward your body and so pressing the blades of the oars against the water toward the stern, while pushing with your feet against a brace. In backing water you reverse the action of the oars, pushing the handles away from your body and pressing the blades of the oars against the water toward the bow.
Turning
To turn your boat to the right, when pulling, you row only with the left oar; or, if you wish to make a sharp turn “pull” with the left oar and “back water” with the right. To turn your boat to the left the action of the oars is reversed.
Feathering
To prevent the momentum of the boat from being checked by the wind blowing on the blades of the oars, the blades must be turned into a horizontal position as they leave the water. In “pulling” this is done by turning the hands backward at {181} the wrist, and in backing water it is done by turning the hands forward at the wrist.
Sculling
To scull is to propel a boat by a single oar at the stern. The boat must be provided with rowlock or a semicircular scoop in the stern, and the boat is propelled by working the oar at the stem, obliquely from side to side. This is a convenient way of doing when you are working among boats in the water, and have to go short distances without the necessity of speed.
Steering
When rowing a boat without the use of a rudder, instead of constantly turning the head around to see where you are going, it is convenient to fix upon some object in the landscape on an imaginary line with the middle of the stern and the middle of the bow; you can then keep your boat approximately in the right position, without the trouble of turning your head, by keeping the object selected on a line with the middle of the stern board.
Coming Alongside
When coming alongside of a boat or wharf always approach on the leeward side or that opposite from which the wind is blowing, and come up so that the boat will be headed into the wind and waves. Stop rowing at a convenient distance from the landing-place and come up with gentle headway; then take in the oar nearest the landing, and, if necessary, back water with the other oar.
Keeping Stroke
When two or more are rowing together the length and speed of the stroke are set by the man sitting nearest the stern.
Rough Weather
Always try to row as nearly as possible into the waves at right angles. In this way you are likely to ship less water and to avoid capsizing.
Going Ashore
When going ashore always leave your oars lying flat on the thwarts on either side of your boat.
The Salute
To salute a passing vessel or boat, hold the oars up at right angles with the water.
Every row-boat should be provided with a rough sponge and a tin dipper to be used in bailing out the water. Always bail out the water after a rain and keep your boat clean and tidy.
Sailing in Small Boats
The most convenient kind of a boat to learn to sail in is a cat-boat, which is a boat with a single fore and aft sail held in place by a boom at the bottom and a gaff at the top.
To understand the principle of sailing we must realize that a sail-boat, without the use of a rudder, acts in the water and wind very much the way a weather vane acts in the air. The bow of the boat naturally turns toward the wind, thus relieving the sail of all pressure and keeping it shaking. But if by keeping the main sheet in your hand you hold the sail in a fixed position, and, at the same time, draw the tiller away from the sail, it will gradually fill with air beginning at the hoist or mast end of the sail and impel the boat in the direction in which you are steering. Given a certain direction in which you want to travel, the problem is, by letting out or hauling in your main-sheet, to keep the sail as nearly as possible at right angles with the direction of the wind. We must remember, also, that, while the sail must be kept full, it should not be kept more than full; that is, its position must be such that, by the least push of the tiller toward the sail, the sail will begin to shake at the hoist. It is even desirable in a strong wind, and especially for beginners, to always let the sail, close to the mast, shake a little without losing too much pressure. When you are sailing with the wind coming over the boat from its port side you are sailing on the port tack, and when you are sailing with the wind coming across the boat on its starboard side you are sailing on the starboard tack. The port side of the boat is the left hand side as you face the bow while standing on board, and the starboard side is the right hand side. An easy way of remembering this is by recalling the sentence, “Jack left port.”
Direction of Wind
Of course, you will see that, if you should forget which way the wind is blowing, you could not possibly know the right position for your sail; and this is one of the first requirements for a beginner. It is quite easy to become confused with regard to the direction of the wind, and therefore every boat should be provided with a small flag or fly at its mast-head and you should keep watching it at every turn of the boat until the habit {183} has become instinctive. It is convenient to remember that the fly should always point as nearly as possible to the end of the gaff, except when you are sailing free or before the wind.
Close to Wind
Sailing with the boat pointing as nearly as possible against the wind is called sailing close to the wind; when you have turned your bow to the right or left so that the wind strikes both boat and sail at right angles you are sailing with the wind abeam; as you let out your sheet so that the boom makes a larger angle with an imaginary line running from the mast to the middle of the stern you are sailing off the wind; and, when your sail stands at right angles to this same line, you are sailing free or before the wind.
Before the Wind
Sailing free, or before the wind, is the extreme opposite of sailing close hauled or on the wind, and the wind is blowing behind your back instead of approaching the sail from the direction of the mast. If you are sailing free on the port tack, with the boom at right angles to the mast on the starboard side, and you should steer your boat sufficiently to starboard, the wind would strike the sail at its outer edge or leech and throw the sail and boom violently over to the port side of the mast. This is called jibing and is a very dangerous thing; it should be carefully guarded against whenever sailing before the wind.
Reefing
If you find that the wind is too strong for your boat, and that you are carrying too much sail, you can let her come up into the wind and take in one or two reefs. This is done by letting out both the throat and peak halliards enough to give sufficient slack of sail, then by hauling the sail out toward the end of the boom, and afterward by rolling the sail up and tying the points under and around it, but not around the boom. Always use a square or reef knot in tying your reef points. In case of a squall or a strong puff of wind, remember that you can always ease the pressure on your sail by turning the bow into the wind, and if for any reason you wish to shorten suddenly you can drop your peak by loosening the peak halliards.
Ready About
Before “going about,” or turning your bow so that the wind will strike the other side of the sail at its mast end, the man {184} at the helm should always give warning by singing out the words, “ready about.” “Going about” is just the opposite of jibbing.
Right of Way
When two boats approach each other in opposite directions, close hauled, the boat on the starboard tack has the right of way and should continue her course. The responsibility of avoiding a collision rests with the boat sailing on the port tack. But a boat running before the wind must always give way to a boat close hauled.
When sailing through high waves, always try as far as possible to head into them directly at right angles. Always steer as steadily as possible. If you are careful to keep the boat on her course and do not let your mind wander, only a slight motion of the tiller from side to side will be necessary.
Flying the Flag
While the “fly” or “pennant” is carried at the top of the mast, the flag is carried at the peak or upper corner of the sail at the end of the gaff. The salute consists of tipping or slightly lowering the flag and raising it again into position.